Basic introduction to baking soda and its properties
Release time:
2020-04-10
Basic introduction to baking soda

Sodium bicarbonate (chemical formula: NaHCO₃), commonly known as baking soda, soda powder, soda powder (Hong Kong, Taiwan), heavy Cao, baking alkali, etc., white fine crystals, the solubility in water is less than soda. Sodium bicarbonate, a white alkaline powder that is easily soluble in water, starts to work after combining with water to release carbon dioxide, reacts faster in acidic liquids (such as fruit juice), and as the ambient temperature increases, The faster the action of the released gas. Sodium bicarbonate will remain sodium carbonate after the action, and the use of too much will cause the finished product to have an alkaline smell. Sodium bicarbonate aqueous solution is weakly alkaline, commonly known as baking soda and baking alkali.
Chemical Properties of Baking Soda
Easily decomposed by heat. Decomposes slowly in moist air. The reaction starts at about 50°C to generate carbon dioxide, and at 100°C, all of it becomes sodium carbonate. It decomposes rapidly in weak acid, and its aqueous solution begins to decompose carbon dioxide and sodium carbonate at 20 ° C, and all decomposes when it reaches the boiling point. It is soluble in 10 parts of water at 25°C, soluble in 12 parts of water at about 18°C, and insoluble in ethanol. The unstirred solution made of cold water has only a slight alkaline reaction to the phenolphthalein test paper, and the alkalinity increases when the temperature is placed or raised. The pH value of the freshly prepared 0.1 mol/L aqueous solution at 25°C is 8.3.
Physical Properties of Baking Soda
Sodium bicarbonate is white crystal, or opaque monoclinic fine crystal. Specific gravity 2.15g. Odorless, salty, soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol. Its aqueous solution is slightly alkaline due to hydrolysis, easy to decompose when heated, rapidly decomposes above 65°C, completely loses carbon dioxide at 270°C, no change in dry air, and slow decomposition in humid air. Solubility: 7.8g, 18°C; 16.0g, 60°C. The ignition point is not flammable, but it needs to be dry, protected from light, and stored in an airtight seal.
Attached is the product quality supervision, inspection and testing report of Henan Province:
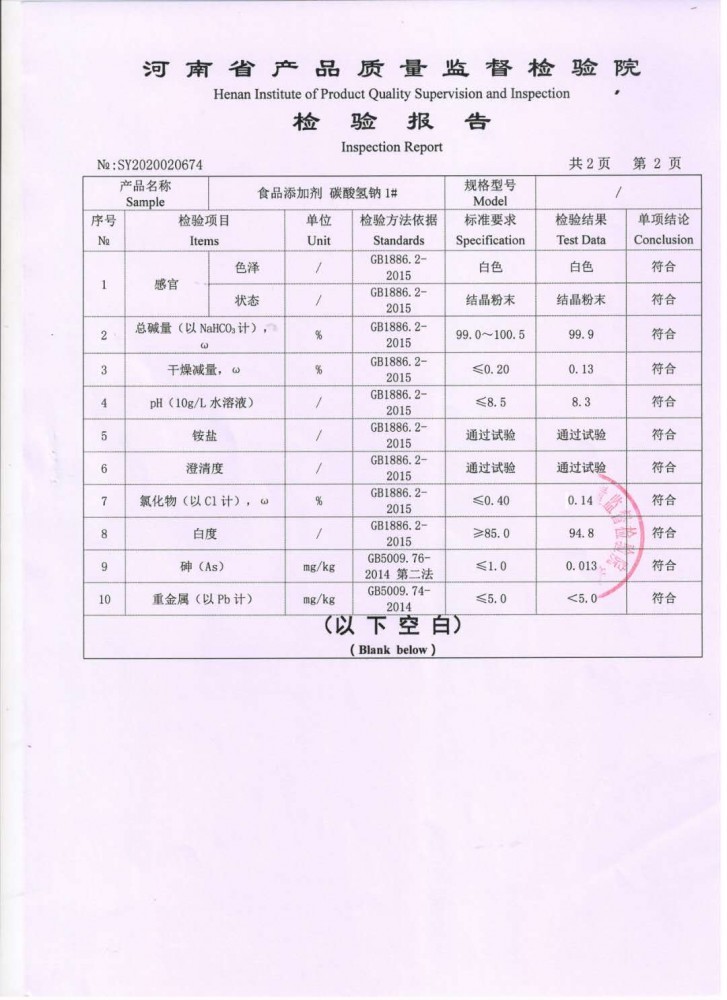
(Disclaimer: The article comes from the Internet and does not represent the views and positions of this site. The copyright belongs to the original author and the original source. If there is any infringement or objection, please contact to correct or delete it.)
Previous article
Related News


